Dec 15, 2025
RuTube Videos Share Malware Disguised as Roblox Cheat Tools
In videos showcasing Roblox cheat tools on RuTube, viewers are directed to download files that sneak malware onto their devices
TLDR
Russian video-sharing platform RuTube hosts many videos advertising free “cheat tools” for Roblox, a popular online gaming platform.
These videos direct viewers to download links for cheat tools, many of which are malicious and contain trojan and stealer malware.
Those behind these schemes are targeting Roblox’s user base, a majority of whom are children – a particularly vulnerable demographic – which raises additional concerns.
Introduction
RuTube is a Russian video-sharing platform and alternative to YouTube. Founded in 2006, the platform is owned by Gazprom Media and has been known for hosting state-authored talking points and propaganda among other user videos.¹
More recently, RuTube has been the host of an array of user videos advertising “cheat tools” for the online gaming platform Roblox. These videos include in-game footage of the cheat tools’ functionality and offer viewers links to download the tools for themselves. Some of these links are legitimate, but others are malicious, leading viewers to accidentally install secret malware onto their devices.
Of particular concern to our researchers in this case was the fact that this scheme targeted such a vulnerable demographic, as a large portion of Roblox’s user base are children.² To gain insight into this unusual malware scheme, Open Measures investigated the activity around the RuTube videos mentioned above as well as the accounts behind them, the download links they directed viewers to, and the relative safety of the files those linked hosted.
Background
Roblox is a massively-multiplayer online (MMO) gaming platform offering users tools to build their own games, share them with others, and socialize in the game’s virtual world. The game is wildly popular around the world, with 111.8 million daily active users (according to company numbers).³
As with many other open-world, MMO-style games, a wide range of Roblox cheating tools and mods are available to users online, shared through various online channels. While many of the cheat tools we uncovered were simply scripts to “hack” aspects of Roblox’s virtual environment for some desired effect (e.g., allowing a player’s avatar to jump higher than usual), the use of cheat tools of any kind is a violation the terms of Roblox’s user agreement.
Regardless, this report does not assess the general uses of Roblox cheat tools or all of their implications. Below, our only interest in the potential harms or risks of using Roblox cheat tools is as a possible attack vector or malware delivery vehicle. Our primary purpose below was to assess what seemed to be a novel strategy: By infiltrating Roblox communities, threat actors could camouflage themselves while sharing their links to cheat tools containing malware by doing so among other channels’ comparatively legitimate links without it.
Methodology
Prevalence on RuTube
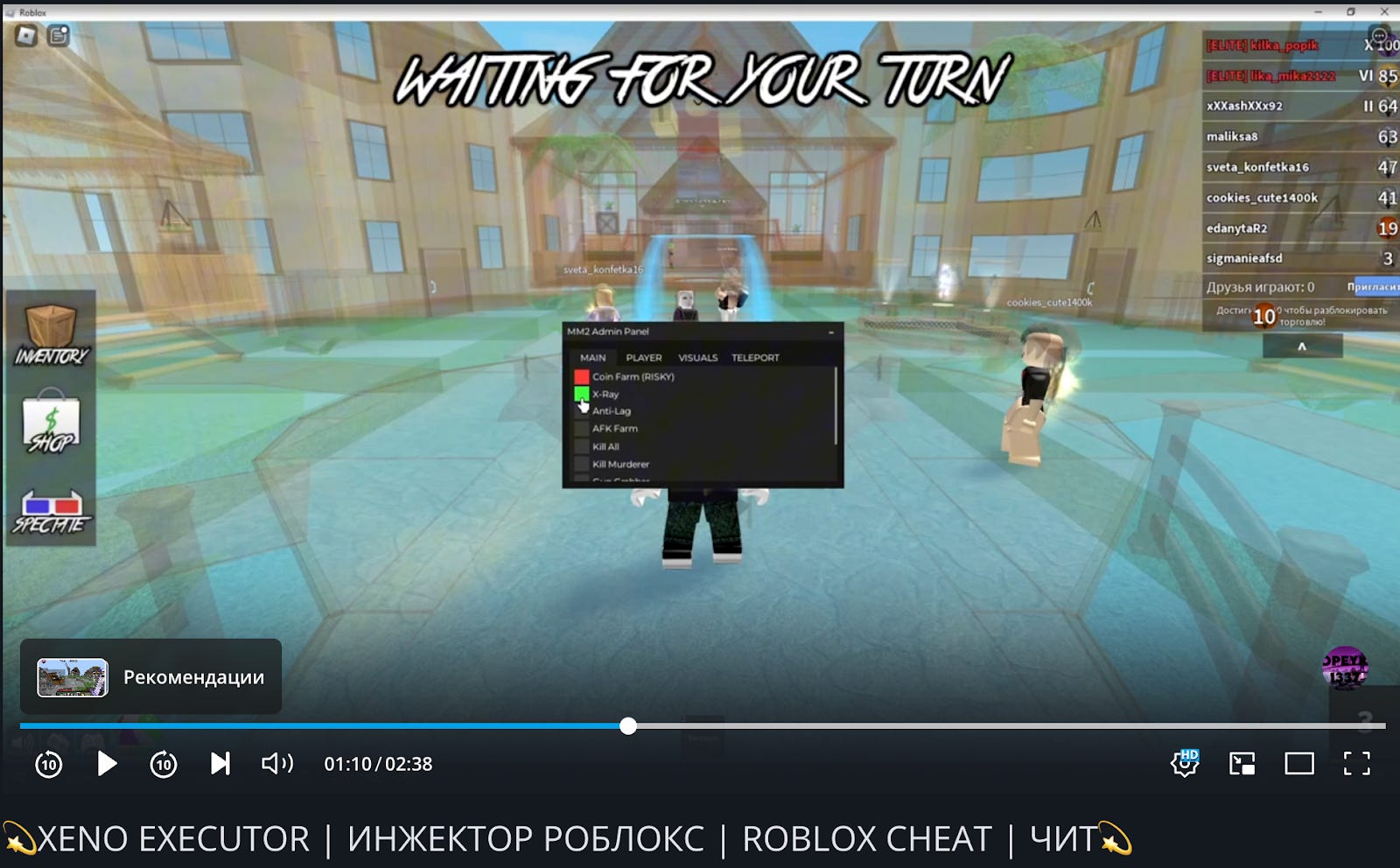
Caption: A RuTube video demonstrating how the “Xeno Executor” can be used in Murder Mystery 2, a popular Roblox game.
Though there are a variety of Roblox cheat tools, our investigation focused on tools marketed as “executors” (such as “Xeno Executor”) and “injectors,” tools which allow users to customize, alter, or manipulate Roblox’s game environment.
From an initial overview of our monitored sources, our researchers found that discussions of executors and injectors aimed at Roblox users were particularly popular on RuTube. To collect various data from these videos and discussions on RuTube, we used the following query:
This query surfaced a range of videos mentioning Roblox cheat tools in their titles, many of which included play-through footage demonstrating the tools’ functionalities. The description boxes below these videos also contained links viewers could visit, ostensibly to download the tools for themselves.
Malicious vs. Non-Malicious Files
Our researchers selected 10 RuTube videos showcasing Roblox executors and injectors from the results we surfaced. Though these videos were selected at random, all of them included some kind of link in the video description.
To get a sense of how many of these were links to malware, we downloaded the files behind all of the links and uploaded everything we collected to VirusTotal, a free service which helps users determine whether a file may be malicious (by running the files through dozens of anti-virus services, aggregating the results, and returning a “detection score” of how many services flagged the files as malicious).⁴
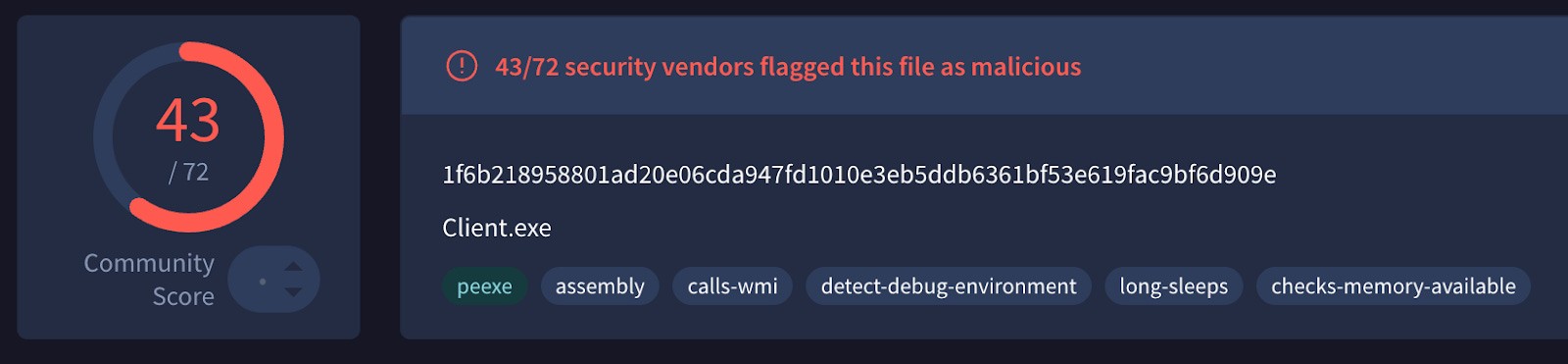
Caption: A VirusTotal report for one of the analyzed files found that 43 of 72 security vendors detected the file as malicious.
Though VirusTotal’s results can help users determine a file’s relative safety, a detection score of zero does not definitively mean a file is not or does not contain malware, as malware creators have developed many specific techniques to evade these detections. As such, researchers should use extreme caution before replicating our research methodology here or opening any seemingly “safe” files downloaded from suspicious sources.
VirusTotal Results
Of the 10 videos we selected, seven had links we could access to download files, though two of the downloaded files ended up being the same file (Sample 5, below). Removing the duplicate file resulted in six distinct files to analyze, of which two appeared to be non-malicious (though one was only downloadable through a suspicious host site with many popup windows, raising concerns about both the site and possibly the file) and four that were flagged as malicious.
Below are the hash values associated with each file we analyzed:
Likely Non-Malicious
1. [fd2a374c2b208295c3b582e7caa2eb65479348d4f34016dcb61ee8dc34894755]⁵
2. [0e6a791aaf1de1e4d9befe2a1da50b4a52c2ed1bd453edd3ffd5226df29e4e06]⁶
Note: Though VirusTotal reported a detection score of 0/72 for Sample 2 above, the file could only be downloaded from a suspicious website with many popups, suggesting the site may be insecure or compromised and casting some doubt on the file’s overall safety.
Malicious
3. [e43cdf862e1153a6b05a0d4aa22a22897e34252d625cee370b5b67c224139ea8]⁷
[423c30a05ccd3675c60fccc4a6c6bd759c882d01097a267bd051e03995c528e5]⁸
[3688a03766109f966bc31c91c11d305b072099d2ae1c63f9a5c4034e4bb37ef6]⁹
[1f6b218958801ad20e06cda947fd1010e3eb5ddb6361bf53e619fac9bf6d909e]¹⁰
For clarity, the below will use the numbers from the list of samples above as shorthand to refer to specific samples (e.g., “Sample 1” refers to hash value [fd2a374c2b208295c3b582e7caa2eb65479348d4f34016dcb61ee8dc34894755]).
Trojan Malware and Stealers
More specifically, VirusTotal flagged our four malicious files as trojan horse malware. Named for its similarities to the Trojan Horse of Greek mythology, trojan malware masquerades as one type of software (in this case, a Roblox cheat tool) while simultaneously serving as a vector for other unauthorized activity (a malware program that can run invisibly and undetected in the background of a user device).¹¹
VirusTotal’s aggregated services also indicated the four malicious files as likely trojan “stealers,” a specific kind of malware that can secretly collect a wide range of valuable information from a target (e.g., log-in credentials, payment card information, cookies, API keys, etc.). For example, Sample 4 was identified via VirusTotal’s aggregated anti-virus services as Salat Stealer, one specific “family” of stealer malware.¹²
Open Measures previously reported on how stealer malware gangs sell access to information stolen with Malware through “marketplaces” on Telegram. In a sense, this kind of activity is a later, point-of-sale stage in a similar kind of cybercrime pipeline. In this investigation, the threat actors sharing links to malware via RuTube video descriptions are operating at an earlier stage of the pipeline (as cyber thieves stealing the sensitive information to later be repackaged and sold).
RuTube Response and Moderation
Notably, of our four malicious files, only one (Sample 6) came from a description under a RuTube video that was still online at the time of writing. The other four (Samples 3, 4, and 5) were found in Open Measures’ indexed RuTube data; their corresponding videos were no longer online, though the channels that posted them still were.
One of these channels is “Moryak Team,” which shared two of the malware samples we examined (Samples 3 and 4) and is still uploading videos to RuTube at the time of writing. At the time of writing, the channel's most recent video, from Dec. 7, 2025, alleged that it could help users circumvent Russia’s recent Roblox ban, passed on Dec. 4, 2025.¹³ The video’s description also contains an additional link not mentioned above but also leads users to download one of the malicious files we scanned (Sample 3).¹⁴

Caption: A recent video from the Moryak Team claiming to help users bypass Russia’s Roblox ban.
Conclusion
RuTube videos showcasing Roblox cheat tools often dupe viewers into downloading hidden malware programs to steal their data; from a security perspective, this is particularly concerning given that the majority of Roblox’s users are children, a demographic that may underestimate or be unaware of the risks associated with downloading Roblox cheat tools, or that may be more likely to make security mistakes online (likely exposing the adults in their family to these risks as well through saved payment cards and other sensitive information).
The impact of Russia’s ban on Roblox is likely to have some impact on this landscape of malicious file sharing in Roblox communities, though to what extent remains unclear and could be the subject of further research. As demonstrated by the Moryak Team example, however, threat actors have wasted no time in using the ban as new leverage to lure in victims.
Citations
Source library. (n.d.). Open Measures. Accessed Dec. 10, 2025. Here.
Baszucki, D. (2023, May 17). Our Vision for All Ages. Roblox. Here.
Tornow, N. (2025, Sept. 4). Rapport annuel sur l’impact économique de Roblox. Roblox. Here.
VirusTotal. (n.d.). How it works. VTDOC. Accessed Dec. 10, 2025. Here.
VirusTotal. (n.d.). Retrieved Dec. 10, 2025. Here.
VirusTotal. (n.d.). Retrieved Dec. 10, 2025. Here.
VirusTotal. (n.d.). Retrieved Dec. 10, 2025. Here.
VirusTotal. (n.d.). Retrieved Dec. 10, 2025, Here.
VirusTotal. (n.d.). Retrieved Dec. 10, 2025, Here.
VirusTotal. (n.d.). Retrieved Dec. 10, 2025. Here.
Australian Signals Directorate. (2023, Nov. 10). Malware. Here.
Unmasked: Salat Stealer – A Deep Dive into Its Advanced Persistence Mechanisms and C2 Infrastructure. (2025, Sept. 5). Cyfirma. Here.
Chia, O. (2025, Dec. 4). Russia bans Roblox over concerns about safety and extremist content. BBC. Here.
VirusTotal. (n.d.). Retrieved Dec. 10, 2025. Here.
Identify online harms with the Open Measures platform.
Organizations use Open Measures every day to track trends related to networks of influence, coordinated harassment campaigns, and state- backed info ops. Click here to book a demo.
